Coral reefs in Hainan Island are very important and are suffering the influences from climate change and anthropogenic activities. Recent studies demonstrated that both climate change and anthropogenic activities are detrimental to coral reefs in Hainan Island, which was based on 5-year field studies by Professor Huang Hui and Dr. Li Xiubao from South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Climate change often causes ocean warming, flooding and increasing of typhoon intensity and frequency, which leads to important influences on coral reef ecosystem. In Sanya, coral bleaching was firstly detected in 2010 due to abnormal seawater temperature rise (2~3°C); however, as Qiongdong Upwelling brings cold water to surface in southern and eastern Hainan Island, coral bleaching has limited impacts on coral reefs there. Recent study also reported that severe flood can change environmental condition and then cause severe detrimental effects on coral reefs; however, the coral reefs recovered very slowly following the flood. Related studies were published at Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management 2012, 15, 227-233 and Marine Biology Research 2013, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17451000.2013.841942.
Studies from Professor Huang Hui demonstrated that environmental changes induced by human activities can cause severe impacts on coral reef environmental conditions in Hainan Island. Macroalgal δ15N-values are effective indicator for sewage stress on coral condition and nutrient pollution has resulted in seriously negative effects on coral distribution and recruitment in eastern Hainan Island. Furthermore, sedimentation also determined the spatial distributions of Sanya coral reefs. A high sedimentation event confirmed that sediments sourced from ocean projects and land-clearing will cause large amount of coral death. Related studies were published at Botanica Marina 2013,DOI 10.1515/bot-2012-0223,Deep Sea Research II 2013, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.04.015i and Chinese Science Bulletin 2013, 58, 1028-1037.
These research were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(40830850 and 41106141)and the Ocean Public Welfare Scientific Research Project (201005012-6)
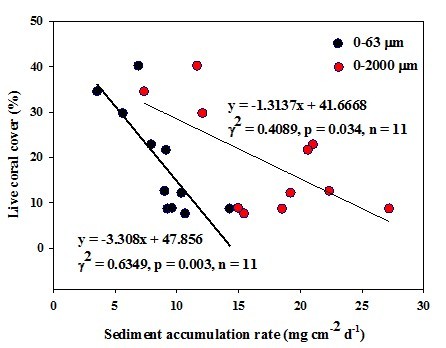
Significantly negative correlations between sedimentation rate and live coral cover on coral reefs in Sanya
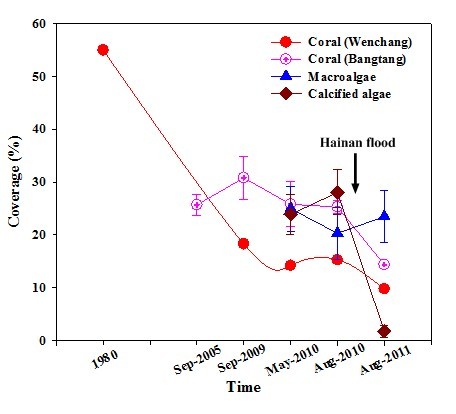
History changes of coverage of live coral, macroalgae and calcified algae on coral reef in Wenchang
