Recent Progress of Internal Solitary Waves in the Northern South China Sea in SCSIO
Recently, the group led by Dr. Cai shuqun published one paper named “A propagation model for the internal solitary waves in the northern south china sea” in the journal of geophysical research(IF=3.082 in the 2009 Journal Citation Reports). The research was funded by the Key Program from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and NSFC.
In this paper, a two-dimensional model describing the propagation of internal solitary waves is developed and the propagation and evolution of the internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea is studied systematically. Simulation reveals the topographic effect, the high and low orders nonlinear effect, the rotation effect, the degree of stratification, the reflection and diffraction of internal solitary wave, the wave-wave interaction and some other key factors on the propagation and evolution of internal solitary waves from deep sea to shallow sea. The simulated result explains the emergence of internal solitary wave in satellite remote sensing image when it propagated from the deep sea to the shallow sea. For example: the polarity reverse, waves from different source go hand in hand to form waves of longer straight crest-lines, and the emergence of wave diffraction, refraction, breaking and re-merged into the new wave series and so on at the two sides of Dongsha island when internal solitary waves encounter it.
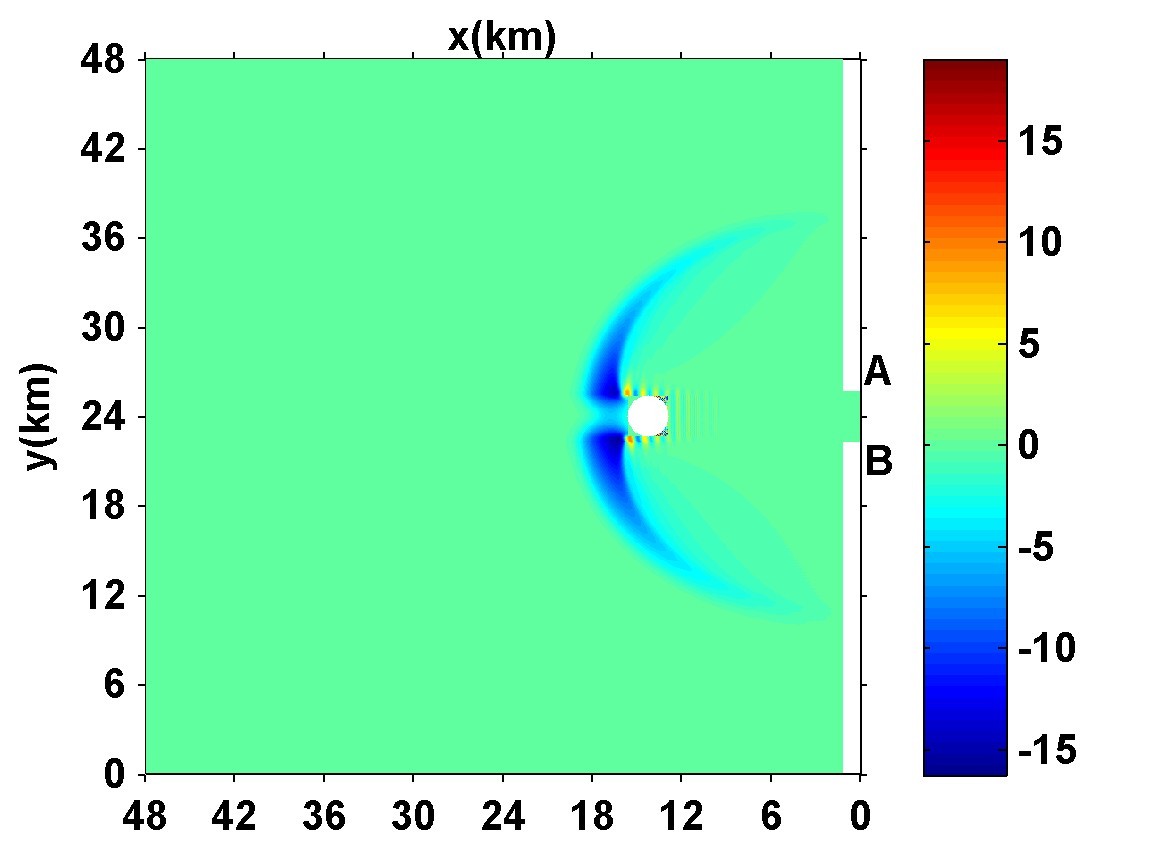
Figure illustration: the Simulated two dimensional westward internal solitary waves(diffraction after interaction with island).